COP30 DeBriefed 21 November 2025: ‘Mutirão’ text latest; ‘Roadmaps’ explained; COP finish times plotted
Multiple Authors
11.21.25Welcome to Carbon Brief’s DeBriefed.
An essential guide to the week’s key developments relating to climate change.
This week
Key ‘mutirão’ text emerges
‘MUTIRÃO’ 2.0: After many late nights, but little progress – and a dramatic fire at the COP30 venue – the much-awaited second draft of the summit’s key agreement, called the “mutirão” text, finally dropped this morning. The new mutirão text “calls for efforts to triple adaptation finance” by 2030 and would launch a presidency-led “Belém mission to 1.5C” alongside a voluntary “implementation accelerator”, as well as a series of “dialogues” on trade. It “decides to establish” a two-year work programme on climate finance, including on a key section of the Paris Agreement called Article 9.1, but has a footnote saying this will not “prejudge” how the climate finance goal agreed last year is met.
Award-winning newsletters
Subscribe to receive the latest developments from leading newspapers, journals and specialist websites, hand-picked and written up by our expert team.
ROADMAPS TO NOWHERE: The latest draft does not refer to the idea of a “fossil-fuel roadmap”, which is not on the COP30 agenda, but has been pushed by Brazil’s president Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva and a group of parties (see below). A letter to the presidency, seen by Carbon Brief and reportedly backed by at least 29 countries, including Colombia, Germany, Palau, Mexico and the UK, says: “We cannot support an outcome that does not include a roadmap [on fossil fuels].” It also flags the lack of a roadmap on deforestation. The letter asks for a revised text.
PLENARY WHEN: The latest draft of the mutirão text is unlikely to be the last. There is also a set of draft decisions that have not been fully resolved. For instance, this morning, the Brazilian COP presidency floated a draft decision on what it is calling the “Belém gender action plan”, with three brackets versus the 496 brackets in the previous version. At a short, informal stocktaking plenary, COP30 president André Corrêa do Lago invited countries to react to the drafts in a “mutirão” meeting, namely, in the “spirit of cooperation”. But expect all timings to be flexible, as they work to iron out differences in closed-door meetings.
Adaptation COP
TRIPLING TARGET: A new text for the global goal on adaptation dropped alongside the mutirão text this morning, after days of tense negotiations. Crucially, it includes the adoption of some of the indicators, which will be used to track countries’ progress on adaptation. Last week, the African Group and others called for the indicators not to be adopted at COP30 – one of the key expectations ahead of the summit – and, instead, a two-year work programme to further refine them due to concerns around adaptation finance.
INDICATORS: The latest text adopts an annex of 59 of the potential 100 indicators, emphasises that they “do not create new financial obligations or commitments” and decides to establish a two-year “Belém-Addis vision” on adaptation to further refine the indicators. The only remaining bracket within the text is to allow for the addition of the final adaptation finance target from the mutirão – which, currently, “calls for efforts to triple adaptation finance compared to 2025 levels by 2030”.
WHAM BAM: The latest text for another key negotiating stream on the “just transition work programme” (JTWP) “decides to develop a just transition mechanism”. This has been a point of particular contention within negotiations. Civil society developed the concept of the Belém Action Mechanism (BAM) over the past year and the G77 and China, a large group of global-south nations, tabled it within the JTWP in the first week. However, there was pushback from the EU, UK and others, with the former instead proposing an “action plan” as an alternative.
CRITICAL MINERALS: While landing on the inclusion of a mechanism is being welcomed by civil society and others, the latest text removes the reference to critical minerals included in its predecessor. If included, it would be the first time a reference to “critical minerals” is adopted in the JTWP.
Around the COP
- Turkey will host COP31, while Australia will take on the presidency and lead the negotiations, under a compromise deal reached between the two nations on Thursday, Reuters reported.
- Brazil set out a plan before COP30 to reform the “action agenda” – which includes 117 “plans to accelerate solutions” outside of the negotiations, covering everything from fossil-fuel phaseout to “sustainable diets for all”. On Wednesday, the presidency rounded off a series of events that have been used to promote this vision.
- China called for the creation of a “practical roadmap” for delivering climate finance by developed countries, which delegation head Li Gao said would help “prevent further erosion of trust between developed and developing countries”.
- An estimated 70,000 people marched in 32C heat in Belém on Saturday, marking the largest COP protest since COP26 in Glasgow.
52
The number of COP30 agenda items that had been agreed by the time DeBriefed was sent to readers.
51
The number of COP30 agenda items not yet agreed.
Latest climate research
- A five-year drought in Iran and around the Euphrates and Tigris basins “would have been very rare” without human-caused climate change | World Weather Attribution
- Integrating nature-based solutions into urban planning could reduce daytime temperatures by 2C during hot periods | Nature Cities
- Warming of the “deep Greenland basin” has exerted “obvious impacts” on the deep waters of the Arctic Ocean | Science Advances
(For more, see Carbon Brief’s in-depth daily summaries of the top climate news stories on Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday and Friday.)
Captured
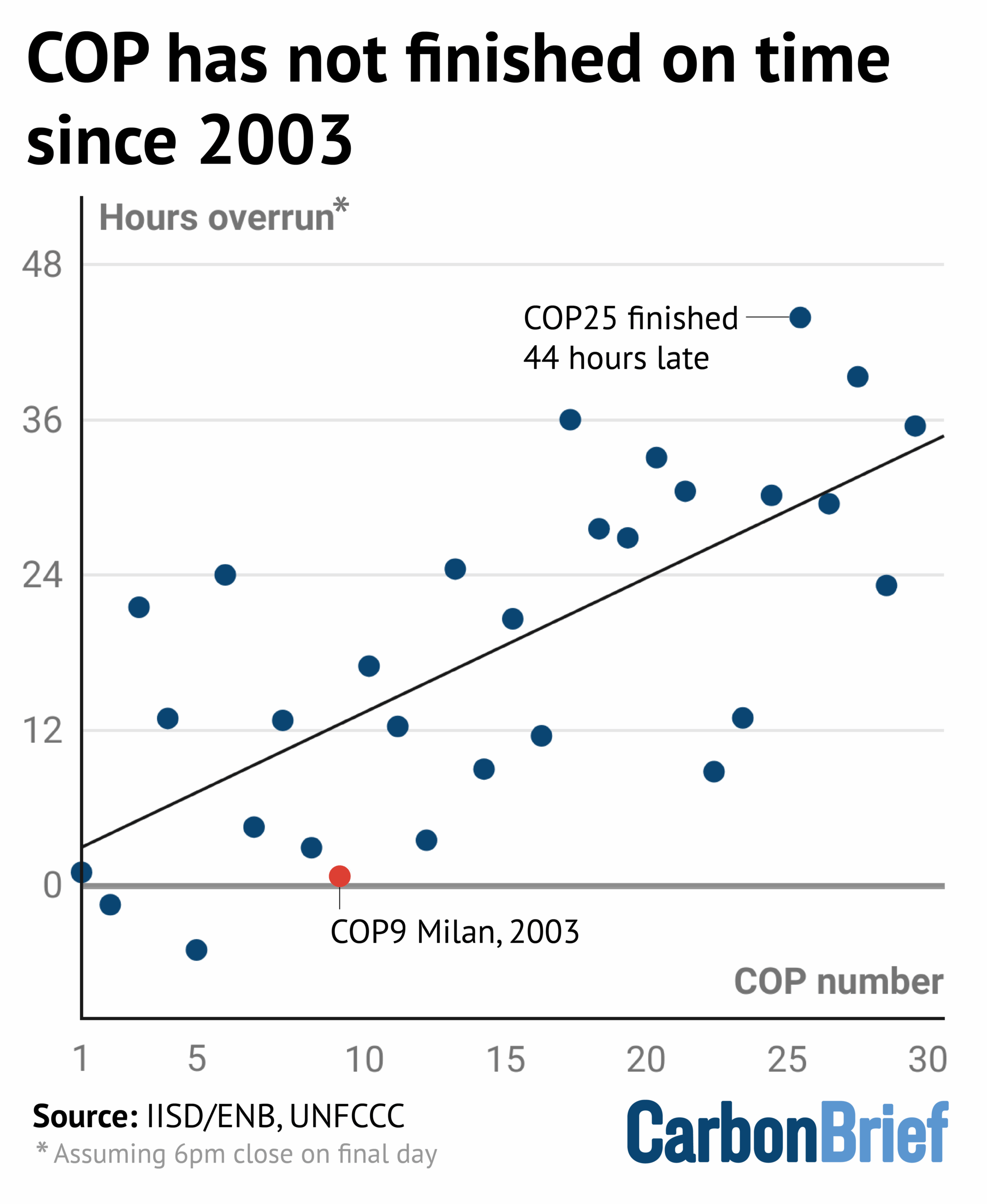
This week saw the Brazilian presidency pledge to conclude some of the most controversial issues at COP30 a whole two days early. In the end, no early deal materialised. As the event approaches its official end time later today, with none of the major negotiations finished, this chart serves to remind that COPs have not finished on time for more than two decades.
Spotlight
‘Roadmaps’ explained
This week, Carbon Brief explains the push for new “roadmaps” away from fossil fuels and deforestation at COP30.
Speaking during the world leaders summit in Belém ahead of COP30, Brazilian president Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva said that the world “need[s] roadmaps to justly and strategically reverse deforestation [and] overcome dependence on fossil fuels”.
His words appeared to spark a movement of countries to call for new roadmaps away from fossil fuels and deforestation to feature as key outcomes of this COP – despite not being on the official agenda for the negotiations.
While momentum for each roadmap has grown, they were referenced only as an option in the first version of COP30’s key text, called the “global mutirão” – and in the second version the reference to roadmaps has disappeared entirely.
Below, Carbon Brief explains the origins of each roadmap, how support for them has grown and how they might feature in COP’s final outcome.
Fossil-fuel roadmap
Most people cite Lula’s pre-COP speech as the start of the movement for a fossil-fuel roadmap.
However, an observer close to the process told Carbon Brief that the COP30 presidency had, in fact, been consulting on the possibility of a roadmap months earlier – drawing help from the Beyond Oil and Gas Alliance, a small group of nations who have pledged to phase out all fossil fuels.
While Brazil was the first country to support the fossil-fuel roadmap, it was joined in the first few days of COP by eight Latin American countries that form the Alliance of Latin America and the Caribbean (AILAC) and by the Environmental Integrity Group (EIG), which includes Mexico, Liechtenstein, Monaco, South Korea, Switzerland and Georgia.
The call for a roadmap was also backed by the Alliance of Small Island States (AOSIS), a group of 39 small low-lying island nations.
As momentum grew, the first global mutirão text appeared on Wednesday 19 November. Paragraph 35 of the text listed three options for where a reference to a fossil-fuel roadmap map might be incorporated, including one option for “no text”.
Later that day, ministers and climate envoys from more than 20 countries united for a packed-out press conference, where they called the current reference to the fossil-fuel roadmap “weak”, adding that it must be “strengthened and adopted”.
At the sidelines of the conference, UK climate envoy Rachel Kyte told journalists that around 80 countries now backed the call for a roadmap. (Carbon Brief obtained the list of 82 countries that have expressed their support.)
However, COP30 CEO Ana Toni told a press conference later that day that a “great majority” of country groups they had consulted saw a fossil-fuel roadmap as a “red line”.
In an interview with Carbon Brief, Dr Osama Faqeeha, deputy environment minister for Saudi Arabia, refused to be drawn on whether a fossil-fuel roadmap was a red line, but said:
“I think the issue is the emissions, it’s not the fuel. And our position is that we have to cut emissions regardless.”
The next day, the EU officially threw its weight behind the call for a fossil-fuel roadmap, after initial delay caused by hesitation to join the movement from Italy and Poland, Climate Home News reported.
The EU circulated its own proposal for how a fossil-fuel roadmap could be referenced in the global mutirão text, the publication added.
However, the latest version of the global mutirão text, released today, does not reference a roadmap at all. It has already sparked condemnation from a range of countries and observers.
It is expected that at least one more iteration of the text will emerge before the COP30 presidency attempts to find agreement, which could see a reference to the roadmap reappear.
Deforestation roadmap
While Lula called for roadmaps away from both fossil fuels and deforestation, the latter has received less attention, with one observer joking to Carbon Brief it had become the “sad forgotten cousin”.
A roadmap away from deforestation was originally only backed by Brazil, the EIG and AILAC.
However, the EU became a relatively early backer – announcing its support for a deforestation roadmap before a fossil-fuel roadmap.
The Democratic Republic of the Congo – one of the world’s “megadiverse” nations and one of the countries responsible for the Congo rainforest – has also announced its support. (See Carbon Brief’s list of supporters.)
As with the fossil-fuel roadmap, a reference to a deforestation roadmap appeared in the first iteration of the mutirão text, but has disappeared from the second. It may – or may not – appear in another version of the text before COP30’s finale.
Watch, read, listen
FOREST TALES: In a new video series from Earthday.org and the Pulitzer Centre, three investigative journalists discussed their reporting on deforestation in Brazil and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
AI IMPACTS: Google CEO, Sundar Pichai, spoke to BBC News about the climate impacts of AI, among other topics.
MISSING DATA: Columnist George Monbiot wrote in the Guardian about the “vast black hole” of climate data in some parts of the world – which he says is a “gift” to climate deniers.
Coming up
- 22-23 November: G20 summit, Johannesburg, South Africa
- 24 November-5 December: 20th meeting of the Conference of the Parties to the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES), Samarkand, Uzbekistan
- 24-29 November: 11th session of the governing body of the International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture, Lima, Peru
Pick of the jobs
- Department for Energy Security and Net Zero, chief press officer | Salary: £60,620-£67,565. Location: London
- World Bank Group, climate change specialist | Salary: Unknown. Location: New Delhi, India
- University of Buffalo, Center for Climate Change and Health Equity, postdoctoral associate | Salary: $50,000-$55,000. Location: Buffalo, New York
- University of Oxford, Queens College, junior fellow in climate change research | Salary: £37,694. Location: Oxford, UK
DeBriefed is edited by Daisy Dunne. Please send any tips or feedback to [email protected].
This is an online version of Carbon Brief’s weekly DeBriefed email newsletter. Subscribe for free here.