DeBriefed 5 September 2025: Pakistan floods hit 1.8m people; UK ‘eco-populism’; How warming threatens a man-made lake
Solomon Elusoji
09.05.25Solomon Elusoji
05.09.2025 | 4:00pmWelcome to Carbon Brief’s DeBriefed.
An essential guide to the week’s key developments relating to climate change.
This week
Pakistan and India floods
EXTREME WEATHER: Heavy flooding forced half a million people to evacuate their homes in just 24 hours in Pakistan’s Punjab this week, the Associated Press reported. It brings the total number of people displaced since last month to 1.8 million, the newswire said. According to Arab News, at least 41 people have died as a result of the flooding since last week. The flooding has also destroyed thousands of acres of crops in Punjab, a province that accounts for 68% of Pakistan’s total annual food grain production, Bloomberg reported.
CROSS-BORDER EVENT: Meanwhile, in Indian Punjab, “at least 30 people have died and more than 354,000 have been affected” by flooding, BBC News reported. India also warned Pakistan about more cross-border flooding for the second time in as many weeks, as both countries reeled from monsoon rains, the Associated Press reported.
UK dividing lines
NEW FACE: Zack Polanski has been elected as the new leader of the Green Party of England and Wales in a landslide victory, the Financial Times reported. Polanski is an “outspoken campaigner who has argued his party needs to ‘connect with people’s anger’ and become more combative against ‘villains’, including oil major Shell and the ‘super-rich’”, the newspaper said. Polanksi wants to “replace” the ruling Labour party on a platform of “eco-populism”, according to BBC News.
NORTH SEA OIL: Meanwhile, the UK Conservative leader Kemi Badenoch pledged to drill “all” of the remaining oil and gas in the North Sea if elected, BBC News reported. [The Conservatives are polling third, at 17%.] In response to the speech, the Daily Telegraph‘s world economy editor Ambrose Evans-Pritchard argued that Badenoch’s plan would not “raise this country’s long-term output of oil and gas by more than homeopathic amounts” nor “move the needle on UK energy prices” (more below).
Around the world
- HIGHER AMBITIONS: The UN urged countries to set new, more ambitious national climate plans this month, ahead of this year’s COP30 summit in Belém, Brazil, Reuters reported.
- ‘JUNK SCIENCE’: A group of more than 85 climate scientists released a “scathing review” of the Trump administration’s misleading climate report, DeSmog reported.
- FOSSIL ENERGY: Russia said China had agreed to a massive new pipeline capable of importing as much as 50bn cubic metres of gas a year, the Financial Times reported.
- US PRESSURE: Reuters reported that the US is pressuring other countries to reject a UN deal on cutting emissions from shipping by threatening them with tariffs, visa restrictions and port levies.
- SWELTERING HEAT: Authorities in Japan and South Korea said 2025 was the hottest summer in their countries since records began, Al Jazeera reported.
- MITIGATION WORK: According to Bloomberg, Zimbabwe has published draft regulations to establish a National Climate Fund. The fund will finance projects “aimed at mitigating the impact of climate change and respond[ing] to emergencies”.
20%
The amount by which clean-energy production has surged in India this year, according to Reuters, citing data from the thinktank Ember.
Latest climate research
- “Extreme cold surges” have “robustly weakened in middle-to-high latitude continents during autumn and winter” due to climate change, according to a study in Nature Communications.
- A study published in npj Climate Action found that exposing people to moral appeals results in overall carbon footprint reduction and increased participation in civic and political climate action, regardless of ideological affiliation.
- The World Bank’s increase in climate finance spending since the Paris Agreement has been driven by projects with “low climate components”, according to a study in Climatic Change.
(For more, see Carbon Brief’s in-depth daily summaries of the top climate news stories on Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday and Friday.)
Captured
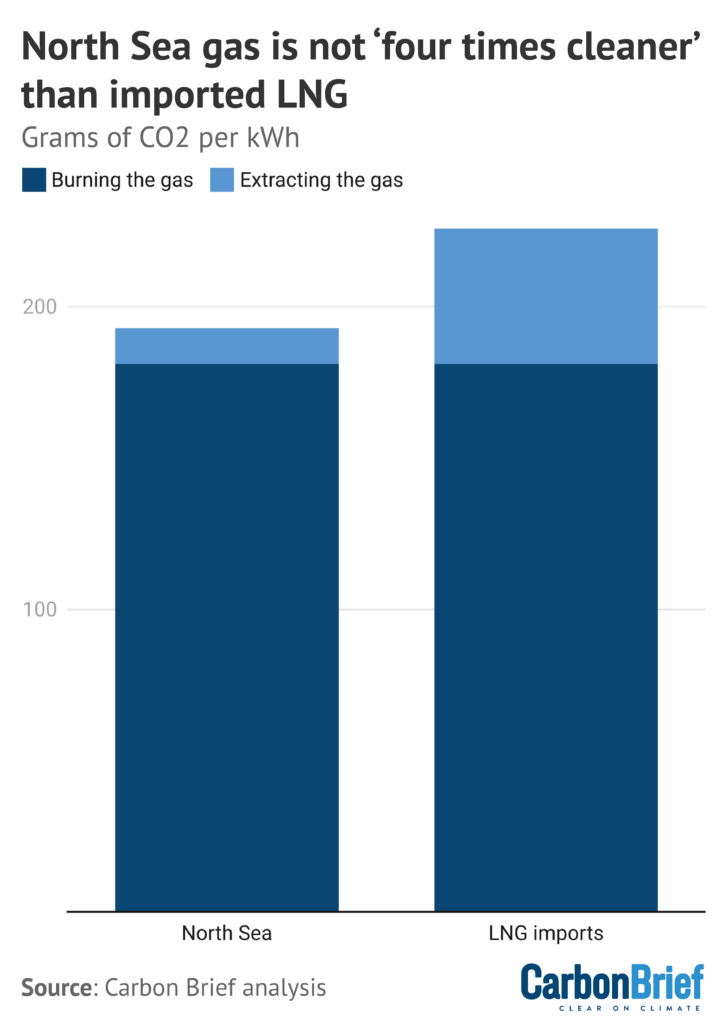
A claim that gas produced in the North Sea emits “four times” less CO2 than imported liquified natural gas (LNG) featured prominently in both the Guardian and the Daily Telegraph this week, following Badenoch’s pledge to drill “all” the remaining oil and gas in the UK. However, this figure is highly misleading. It only refers to the emissions that come from the process of extracting and delivering the gas, which are much smaller than those from burning it. When both extraction and burning of the gas are taken into account, CO2 emissions from UK production are only around 15% lower than those from LNG imports, according to a new factcheck from Carbon Brief.
Spotlight
A man-made lake threatened by climate change
This week, Carbon Brief reports on how climate change is impacting the sustainability of a scenic nature reserve in the southern US.
In 1941, as World War 2 thickened, the US Congress approved a plan to construct a reservoir storage project on the Hiwassee River, a water body that cuts across the states of Georgia, North Carolina and Tennessee.
The dam, which came to be known as Chatuge after an 18th-century Cherokee village, was originally built for power generation purposes. However, after it was completed, it became more than a hydroelectric project.
In May 1942, the Towns County Lions Club started stocking fish in the newly created Lake Chatuge. In 1944, Clay County leased a tract of land for a public park.
Today, the park offers “scenic mountain views” and “panoramic views” of Lake Chatuge. The lake is also home to rare, endangered plant species and is an important source of drinking water.
However, Lake Chatuge’s future has been plunged into uncertainty after the Tennessee Valley Authority proposed a plan to repair the dam’s spillway, which could involve draining the lake’s water levels by 20 feet (6m) for up to eight years.
The TVA’s action is largely forward-thinking. While the dam and its spillway are in good condition, the public utility company is wary of extreme weather events made more likely by climate change.
In September 2024, Hurricane Helene tore through parts of Georgia and North Carolina, leaving more than 128 people dead across the US and uprooting communities in its wake. One analysis estimated that 44% of the economic damage from the storm can be attributed to human-caused climate change.
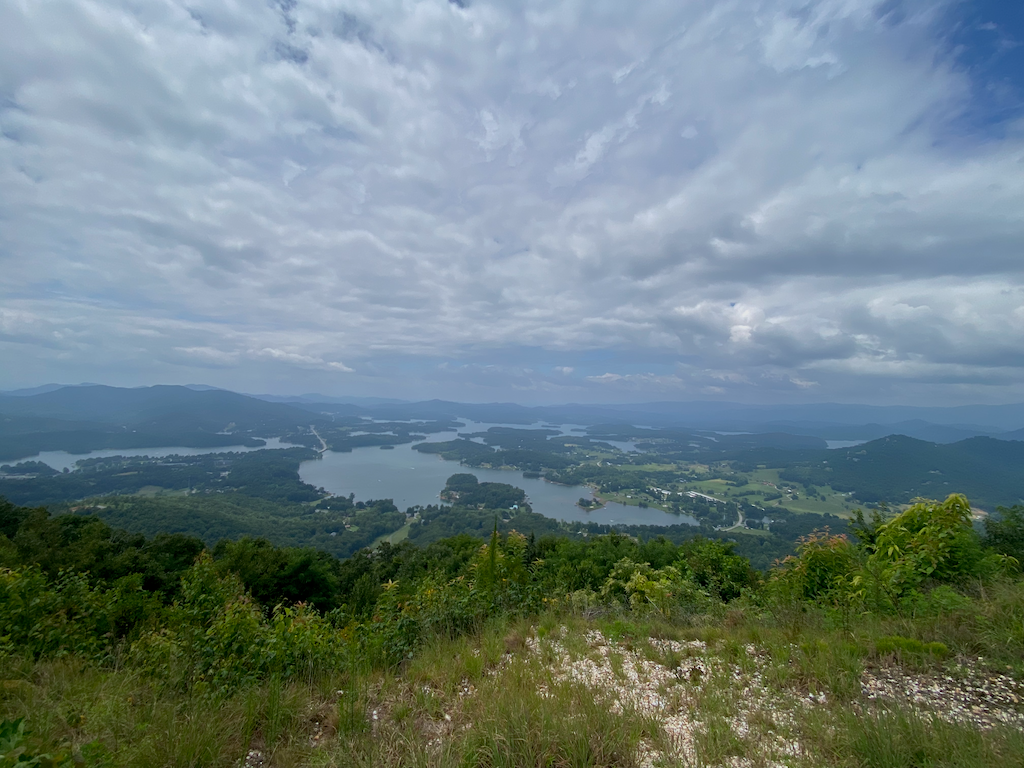

The Lake Chatuge area was largely spared, but officials worry that the next extreme weather event may not be far off.
“It’s the kind of event – the unusual storm event that can happen, that’s pretty rare – is what we’re looking out for,” a TVA project manager has said.
Meanwhile, aside from the imminent repairs made more likely by the increased possibility of extreme weather events, Lake Chatuge is also battling a parrot feather infestation, a phenomenon involving the spread of an invasive plant that has been linked to global warming in other parts of the US.
Saving Lake Chatuge
The threat posed by climate change to Lake Chatuge is not an isolated case. A July 2025 report by researchers at Utah State University found that climate change is affecting the social benefits of dams across the country.
Elsewhere in the world, the impact of extreme weather on ageing dams is wide ranging, including recently heightening tensions between India and Pakistan.
However, community members in the Lake Chatuge area are not giving up easily. A Facebook group dedicated to saving the lake has more than 2,000 members.
“Lake Chatuge is our economy,” Towns County’s sole commissioner, Cliff Bradshaw, told Carbon Brief. He added:
“The main attraction to this area is Lake Chatuge. Without the lake, the county’s tourism would drop, and our economy would suffer greatly – could even drive the county into a depression – as we have a great deal of businesses that rely solely on activities on Lake Chatuge for their customers, such as marinas, party boats and water activity playgrounds. The other businesses in town may not rely on the lake for customers, but do rely on the tourist traffic brought into the area by the lake to drive customers into their place of business.”
According to reporting by the Atlanta-Journal Constitution, visitors have spent up to $100m annually in the area since 2021.
The TVA’s repair work could begin as soon as 2027, but community members are asking both the public utility company and political leaders to help find the least damaging pathway.
Watch, read, listen
SCIENCE CUTS: The Financial Times reported on how the Trump administration has “gutted” the Federal Emergency Management Agency (Fema), throwing into doubt the nation’s ability to respond to extreme weather disasters.
SUSTAINABLE ECONOMICS: In an interview with Le Monde, the French economist Thomas Piketty argued that protecting the planet from climate change requires wealth redistribution.
TWEAKING NATURE: A Havard atmospheric chemist and an Oxford planetary physicist discussed the nuances and subtleties of geoengineering on the podcast Entanglements by Undark.
Coming up
- 8 September: Norway election
- 8-12 September: 54th Pacific Islands Forum Leaders Meeting, Honoraria, Solomon Islands
- 9-23 September: 80th Session of the UN General Assembly, New York
Pick of the jobs
- Energy UK, policy manager | Salary: £38,450. Location: London
- CNN Digital, climate and weather editor | Salary: $91,000-$169,000. Location: Atlanta, Washington DC, New York, Chicago or Burbank, California
- The Post and Courier, rising waters reporter | Salary: Unknown. Location: South Carolina, US
- The Seattle Times, climate reporter | Salary: $75,000-$90,000. Location: Seattle, US
DeBriefed is edited by Daisy Dunne. Please send any tips or feedback to [email protected].
This is an online version of Carbon Brief’s weekly DeBriefed email newsletter. Subscribe for free here.