
Q&A: What UK’s ‘warm homes plan’ means for climate change and energy bills
Multiple Authors
01.23.26Multiple Authors
23.01.2026 | 2:05pmThe UK government has released its long-awaited “warm homes plan”, detailing support to help people install electric heat pumps, rooftop solar panels and insulation in their homes.
It says up to 5m households could benefit from £15bn of grants and loans earmarked by the government for these upgrades by 2030.
Electrified heating and energy-efficient homes are vital for the UK’s net-zero goals, but the plan also stresses that these measures will cut people’s bills by “hundreds of pounds” a year.
The plan shifts efforts to tackle fuel poverty away from a “fabric-first” approach that starts with insulation, towards the use of electric technologies to lower bills and emissions.
Much of the funding will support people buying heat pumps, but the government has still significantly scaled back its expectations for heat-pump installations in the coming years.
Beyond new funding, there are also new efficiency standards for landlords that could result in nearly 3m rental properties being upgraded over the next four years.
In addition, the government has set out its ambition for scaling up “heat networks”, where many homes and offices are served by communal heating systems.
Carbon Brief has identified the key policies laid out in the warm homes plan, as well as what they mean for the UK’s climate targets and energy bills.
- Why do homes matter for UK climate goals?
- What is the warm homes plan?
- What is included in the warm homes plan?
- What does the warm homes plan mean for energy bills?
- What has been the reaction to the plan?
Why do homes matter for UK climate goals?
Buildings are the second-largest source of emissions in the UK, after transport. This is largely due to the gas boilers that keep around 85% of UK homes warm.
Residential buildings produced 52.8m tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent (MtCO2e) in 2024, around 14% of the nation’s total, according to the latest government figures.
Fossil-fuel heating is by far the largest contributor to building emissions. There are roughly 24m gas boilers and 1.4m oil boilers on the island of Great Britain, according to the National Energy System Operator (NESO).
This has left the UK particularly exposed – along with its gas-reliant power system – to the impact of the global energy crisis, which caused gas prices – and energy bills – to soar.
At the same time, the UK’s old housing stock is often described as among the least energy efficient in Europe. A third of UK households live in “poorly insulated homes” and cannot afford to make improvements, according to University College London research.
This situation leads to more energy being wasted, meaning higher bills and more emissions.
Given their contribution to UK emissions, buildings are “expected to be central” in the nation’s near-term climate goals, delivering 20% of the cuts required to achieve the UK’s 2030 target, according to government adviser the Climate Change Committee (CCC).
(Residential buildings account for roughly 70% of the emissions in the buildings sector, with the rest coming from commercial and public-sector buildings.)
Over recent years, Conservative and Labour governments have announced various measures to cut emissions from homes, including schemes to support people buying electric heat pumps and retrofitting their homes.
However, implementation has been slow. While heat-pump installations have increased, they are not on track to meet the target set by the previous government of 600,000 a year by 2028.
Meanwhile, successive schemes to help households install loft and wall insulation have been launched and then abandoned, meaning installation rates have been slow.
At the same time, the main government-backed scheme designed to lift homes out of fuel poverty, the “energy company obligation” (ECO), has been mired in controversy over low standards, botched installations and – according to a parliamentary inquiry – even fraud.
(The government announced at the latest budget that it was scrapping ECO.)
The CCC noted in its most recent progress report to parliament that “falling behind on buildings decarbonisation will have severe implications for longer-term decarbonisation”.
What is the warm homes plan?
The warm homes plan was part of the Labour party’s election-winning manifesto in 2024, sold at the time as a way to “cut bills for families” through insulation, solar and heat pumps, while creating “tens of thousands of good jobs” and lifting “millions out of fuel poverty”.
It replaces ECO, introduces new support for clean technologies and wraps together various other ongoing policies, such as the “boiler upgrade scheme” (BUS) grants for heat pumps.
The warm homes plan was officially announced by the government in November 2024, stating that up to 300,000 households would benefit from home upgrades in the coming year. However, the plan itself was repeatedly delayed.
In the spending review in June 2025, the government confirmed the £13.2bn in funding for the scheme pledged in the Labour manifesto, covering spending between 2025-26 and 2029-30.
The government said this investment would help cut bills by up to £600 per household through efficiency measures and clean technologies such as heat pumps, solar panels and batteries.
After scrapping ECO at the 2025 budget, the treasury earmarked an extra £1.5bn of funding for the warm homes plan over five years. This is less than the £1bn annual budget for ECO, which was funded via energy bills, but is expected to have lower administrative overheads.
In the foreword to the new plan, secretary of state Ed Miliband says that it will deliver the “biggest public investment in home upgrades in British history”. He adds:
“The warm homes plan [will]…cut bills, tackle fuel poverty, create good jobs and get us off the rollercoaster of international fossil fuel markets.”
Miliband argues in his foreword that the plan will “spread the benefits” of technologies such as solar to households that would otherwise be unable to afford them. He writes: “This historic investment will help millions seize the benefits of electrification.” Miliband concludes:
“This is a landmark plan to make the British people better off, secure our energy independence and tackle the climate crisis.”
What is included in the warm homes plan?
The warm homes plan sets out £15bn of investment over the course of the current parliament to drive uptake of low-carbon technologies and upgrade “up to” 5m homes.
A key focus of the plan is energy security and cost savings for UK households.
The government says its plan will “prioritise” investment in electrification measures, such as heat pumps, solar panels and battery storage. This is where most of the funding is targeted.
However, it also includes new energy-efficiency standards to encourage landlords to improve conditions for renters.
Some policies were notable due to their absence, such as the lack of a target to end gas boiler sales. The plan also states that, while it will consult on the use of hydrogen in heating homes, this is “not yet a proven technology” and therefore any future role would be “limited”.
New funding
Technologies such as heat pumps and rooftop solar panels are essential for the UK to achieve its net-zero goals, but they carry significant up-front costs for households. Plans for expanding their uptake therefore rely on government support.
Following the end of ECO in March, the warm homes plan will help fill the gap in funding for energy-efficiency measures that it is expected to leave.
As the chart below shows, a range of new measures under the warm homes plan – including a mix of grants and loans – as well as more funding for existing schemes, leads to an increase in support out to 2030.
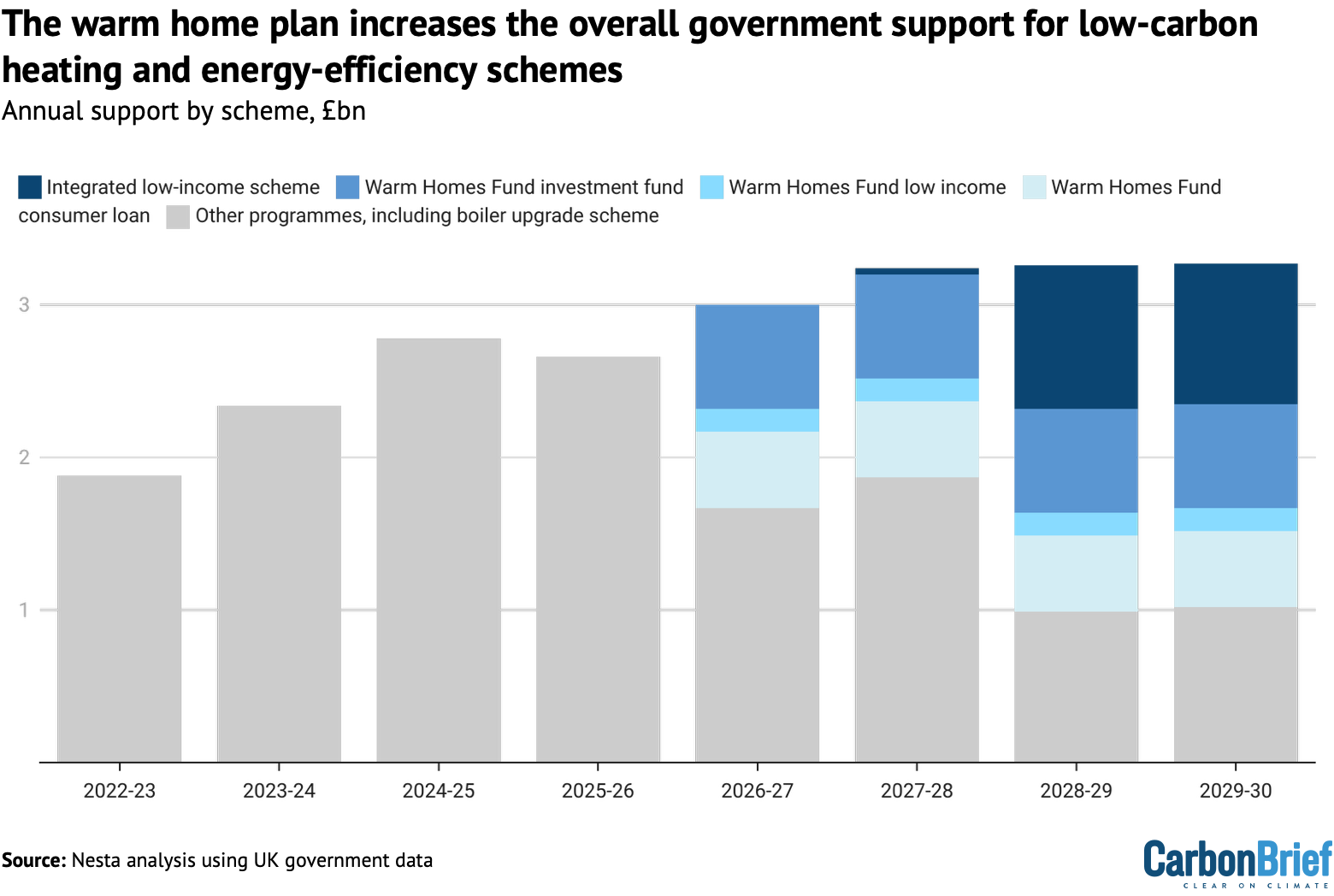
One third of the total funding – £5bn in total – is aimed at low-income households, including social housing tenants. This money will be delivered in the form of grants that could cover the full cost of upgrades.
The plan highlights solar panels, batteries and “cost-effective insulation” for the least energy-efficient homes as priority measures for this funding, with a view to lowering bills.
There is also £2.7bn for the existing boiler upgrade scheme, which will see its annual allocation increase gradually from £295m in 2025-26 to £709m in 2029-30.
This is the government’s measure to encourage better-off “able to pay” households to buy heat pumps, with grants of £7,500 towards the cost of replacing a gas or oil-fired boiler. For the first time, there will also be new £2,500 grants from the scheme for air-to-air heat pumps (See: Heat pumps.)
A key new measure in the plan is £2bn for low- and zero-interest consumer loans, to help with the cost of various home upgrades, including solar panels, batteries and heat pumps.
Previous efforts to support home upgrades with loans have not been successful. However, innovation agency Nesta says the government’s new scheme could play a central role, with the potential for households buying heat pumps to save hundreds of pounds a year, compared to purchases made using regular loans.
The remaining funding over the next four years includes money assigned to heat networks and devolved administrations in Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland, which are responsible for their own plans to tackle fuel poverty and household emissions.
Heat pumps
Heat pumps are described in the plan as the “best and cheapest form of electrified heating for the majority of our homes”.
The government’s goal is for heat pumps to “increasingly become the desirable and natural choice” for those replacing old boilers. At the same time, it says that new home standards will ensure that new-build homes have low-carbon heating systems installed by default.
Despite this, the warm homes plan scales back the previous government’s target for heat-pump installations in the coming years, reflecting the relatively slow increase in heat-pump sales. It also does not include a set date to end the sale of gas boilers.
The plan’s central target is for 450,000 heat pumps to be installed annually by 2030, including 200,000 in new-build homes and 250,000 in existing homes.
This is significantly lower than the previous target – originally set in 2021 under Boris Johnson’s Conservative government – to install 600,000 heat pumps annually by 2028.
Meeting that target would have meant installations increasing seven-fold in just four years, between 2024 and 2028. Now, installations only need to increase five-fold in six years.
As the chart below shows, the new target is also considerably lower than the heat-pump installation rate set out in the CCC’s central net-zero pathway. That involved 450,000 installations in existing homes alone by 2030 – excluding new-build properties.
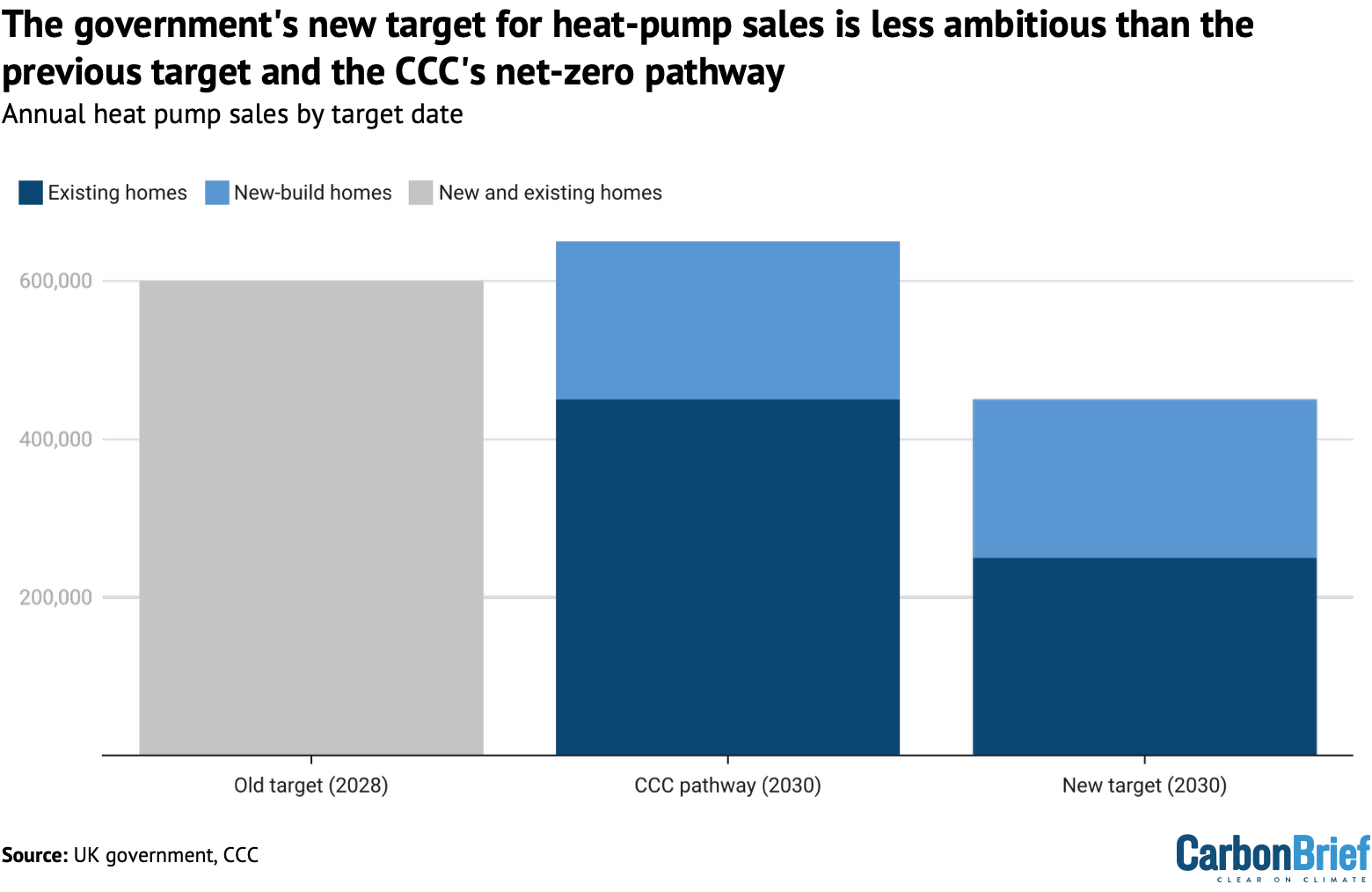
Some experts and campaigners questioned how the UK would remain on track for its legally binding climate goals given this scaled-back rate of heat-pump installations.
Additionally, Adam Bell, policy director at the thinktank Stonehaven, writes on LinkedIn that the “headline numbers for heat pump installs do not stack up”.
Heat pumps in existing homes are set to be supported primarily via the boiler upgrade scheme and – according to Bell – there is not enough funding for the 250,000 installations that are planned, despite an increased budget.
The government’s plan relies in part on the up-front costs of heat pump installation “fall[ing] significantly”. According to Bell, it may be that the government will reduce the size of boiler upgrade scheme grants in the future, hoping that costs will fall sufficiently.
Alternatively, the government may rely on driving uptake through its planned low-cost loans and the clean heat market mechanism, which requires heating-system suppliers to sell a growing share of heat pumps.
Rooftop solar
Rooftop solar panels are highlighted in the plan as “central to cutting energy bills”, by allowing households to generate their own electricity to power their homes and sell it back to the grid.
At the same time, rooftop solar is expected to make a “significant contribution” to the government’s target of hitting 45-47 gigawatts (GW) of solar capacity by 2030.
As it stands, there is roughly 5.2GW of solar capacity on residential rooftops.
Taken together, the government says the grants and loans set out in the warm homes plan could triple the number of homes with rooftop solar from 1.6m to 4.6m by 2030.
It says that this is “in addition” to homes that decide to install rooftop solar independently.
Efficiency standards
The warm homes plan says that the government will publish its “future homes standard” for new-build properties, alongside necessary regulations, in the first quarter of 2026.
On the same day, the government also published its intention to reform “energy performance certificates” (EPCs), the ratings that are supposed to inform prospective buyers and renters about how much their new homes will cost to keep warm.
The current approach to measuring performance for EPCs is “unreliable” and thought to inadvertently discourage heat pumps. It has faced long-standing calls for reform.
As well as funding low-carbon technologies, the warm homes plan says it is “standing up for renters” with new energy-efficiency standards for privately and socially rented homes.
Currently, private renters – who rely on landlords to invest in home improvements – are the most likely to experience fuel poverty and to live in cold, damp homes.
Landlords will now need to upgrade their properties to meet EPC ratings B and C across two new-style EPC metrics by October 2030. There are “reasonable exemptions” to this rule that will limit the amount landlords have to spend per property to £10,000.
In total, the government expects “up to” 1.6m homes in the private-rental sector to benefit from these improvements and “up to” 1.3m social-rent homes.
These new efficiency standards therefore cover three-fifths of the “up to” 5m homes helped by the plan.
The government also published a separate fuel poverty strategy for England.
Heat networks
The warm homes plan sets out a new target to more than double the amount of heating provided using low-carbon heat networks – up to 7% of England’s heating demand by 2035 and a fifth by 2050.
This involves an injection of £1.1bn for heat networks, including £195m per year out to 2030 via the green heat network fund, as well as “mobilising” the National Wealth Fund.
The plan explains that this will primarily benefit urban centres, noting that heat networks are “well suited” to serving large, multi-occupancy buildings and those with limited space.
Alongside the plan, the government published a series of technical standards for heat networks, including for consumer protection.
What does the warm homes plan mean for energy bills?
The warm homes plan could save households “hundreds on energy bills” for those whose homes are upgraded, according to the UK government.
This is in addition to two changes announced in the budget in 2025, which are expected to cut energy bills for all homes by an average of £150 a year.
This included the decisions to bring ECO to an end when the current programme of work wraps up at the end of the financial year and for the treasury to cover three-quarters of the cost of the “renewables obligation” (RO) for three years from April 2026.
Beyond this, households that take advantage of the measures outlined in the plan can expect their energy bills to fall by varying amounts, the government says.
The warm homes plan includes a number of case studies that detail how upgrades could impact energy bills for a range of households. For example, it notes that a social-rented two-bedroom semi-detached home that got insulation and solar panels could save £350 annually.
An owner-occupier three-bedroom home could save £450 annually if it gets solar panels and a battery through consumer loans offered under the warm homes plan, it adds.
Similar analysis published by Nesta says that a typical household that invests in home upgrades under the plan could save £1,000 a year on its energy bill.
It finds that a household with a heat pump, solar panels and a battery, which uses a solar and “time of use tariff”, could see its annual energy bill fall by as much as £1,000 compared with continuing to use a gas boiler, from around £1,670 per year to £670, as shown in the chart below.

Ahead of the plan being published, there were rumours of further “rebalancing” energy bills to bring down the cost of electricity relative to gas. However, this idea failed to come to fruition in the warm homes plan.
This would have involved reducing or removing some or all of the policy costs currently funded via electricity bills, by shifting them onto gas bills or into general taxation.
This would have made it relatively cheaper to use electric technologies such as heat pumps, acting as a further incentive to adopt them.
Nesta highlights that in the absence of further action with regard to policy costs, the electricity-to-gas price ratio is likely to stay at around 4.1 from April 2026.
What has been the reaction to the plan?
Many of the commitments in the warm homes plan were welcomed by a broad range of energy industry experts, union representatives and thinktanks.
Greg Jackson, the founder of Octopus Energy, described it as a “really important step forward”, adding:
“Electrifying homes is the best way to cut bills for good and escape the yoyo of fossil fuel costs.”
Dhara Vyas, chief executive of the trade body Energy UK, said the government’s commitment to spend £15bn on upgrading home heating was “substantial” and would “provide certainty to investors and businesses in the energy market”.
On LinkedIn, Camilla Born, head of the campaign group Electrify Britain, said the plan was a “good step towards backing electrification as the future of Britain, but it must go hand in hand with bringing down the costs of electricity”.
However, right-leaning publications and politicians were critical of the plan, focusing on how a proportion of solar panels sold in the UK are manufactured in China.
According to BBC News, two-thirds (68%) of the solar panels imported to the UK came from China in 2024.
In an analysis of the plan, the Guardian’s environment editor Fiona Harvey and energy correspondent Jillian Ambrose argued that the strategy is “all carrot and no stick”, given that the “longstanding proposal” to ban the installation of gas boilers beyond 2035 has been “quietly dropped”.
Christopher Hammond, chief executive of UK100, a cross-party network of more than 120 local authorities, welcomed the plan, but urged the government to extend it to include public buildings.
The government’s £3.5bn public sector decarbonisation scheme, which aimed to electrify schools, hospitals and council buildings, ended in June 2025 and no replacement has been announced, according to the network.





